Selecting the right mold-making material is crucial for successful replication, model making, and creative casting. Tin-cure silicone (also known as condensation-cure silicone) has become a preferred choice for applications ranging from professional craftsmanship to small-batch industrial production, thanks to its balanced performance, user-friendliness, and broad compatibility. This guide provides a systematic overview of its working principle, key characteristics, ideal use cases, and best practices.
How It Works: Condensation Reaction at Room Temperature
Tin-cure silicone is a two-part condensation-cure liquid silicone rubber. It cures via a chemical reaction at room temperature without requiring external heat.
Key Advantage: Its ease of use and significantly lower sensitivity to environmental contaminants (like sulfur or amine compounds) compared to platinum-cure silicones make it ideal for workshop environments or projects involving complex master materials.
Core Properties & Advantages
The effectiveness of tin-cure silicone stems from its optimal balance across several key performance metrics:
1.Exceptional Detail Reproduction
2.Superior Mechanical Strength & Durability
3.Efficient Room-Temperature Cure Process
4.Good Chemical Stability & Broad Material Compatibility
5.Cost-Effectiveness
Common Applications
Its versatility makes tin-cure silicone suitable for diverse fields:
Product Selection Guide
For optimal results, choose the right product specifications based on your project needs:
| Consideration | Recommendation |
| Model Complexity | High detail, undercuts → Choose a low viscosity (high flow) grade. |
| Casting Material | Plaster, wax → Medium hardness (e.g., 20A-30A). |
| Resin, concrete → Higher hardness (e.g., 30A-40A) for shape retention. | |
| Demolding Needs | Deep draws, complex geometry → Choose a softer, more stretchable grade (e.g., 10A-20A). |
| Visual Requirement | Need to see filling progress → Translucent grade. |
| Durability, stain resistance → White or opaque grade. |
Professional Workflow & Safety Guidelines
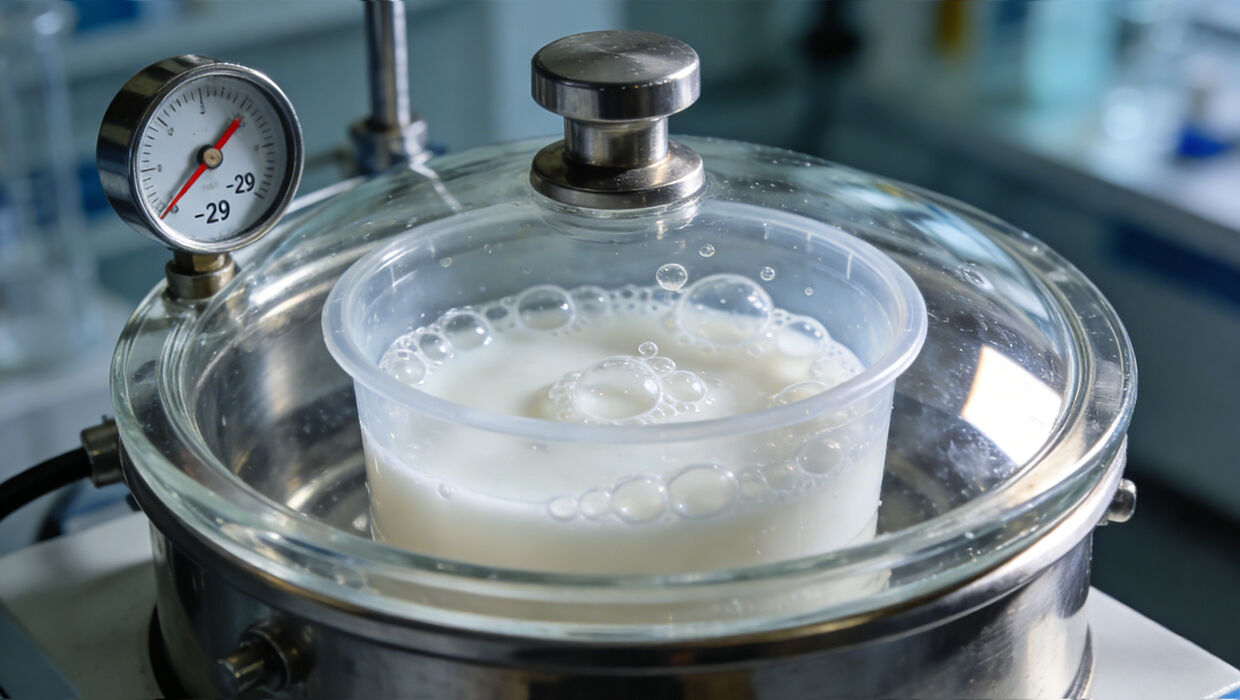
1. Mixing & Degassing

2. Master Model Preparation
3. Curing & Environment
4. Important Safety Notes
Tin-Cure vs. Platinum-Cure: How to Choose?
| Property | Tin-Cure Silicone | Platinum-Cure Silicone |
| Cost | More economical, lower cost per volume | Higher cost |
| Ease of Use | High, less sensitive to contaminants, wider mixing tolerance | Lower, prone to "poisoning" (inhibition), requires precise mixing |
| Cure Byproducts | Yes (alcohols), requires ventilation | None |
| Heat Resistance & Longevity | Good | Superior, typically better long-term heat stability and fatigue resistance |
| Clarity & Anti-Yellowing | Moderate, may yellow slightly over time | Excellent, high clarity and UV/age resistance |
| Ideal Use Cases | Architectural casts, plaster, sulfur-containing clays, large-volume molds, cost-sensitive projects | High-detail resin casting, food-safe applications, optical clarity, long-term high-heat exposure |
Conclusion
Tin-cure silicone remains an indispensable material in modern manufacturing and creative industries due to its excellent cost-performance ratio, reliable handling, and broad material compatibility. Whether you are undertaking an architectural project or crafting detailed artistic pieces, understanding and utilizing this material effectively can significantly enhance both the efficiency and quality of your molding process.
About Jianghe Silicone:
As a professional provider of silicone material solutions, Jianghe Silicone is committed to delivering a stable and high-performance range of tin-cure silicone products. Beyond our standard formulations, we offer flexible customization services (tailoring viscosity, cure speed, hardness, or color) and technical support to meet specific application requirements.

 Hot News
Hot News2025-12-29
2025-11-25
2025-11-23
2025-11-22